  |
  |
|
Seed Development
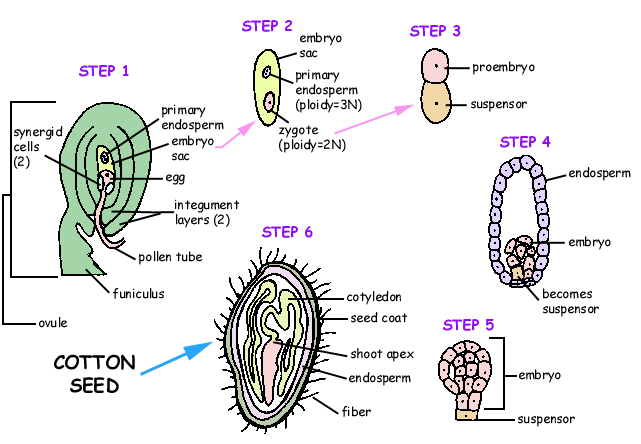
Step 1: Double fertilization occurs in the ovule. In the embryo sac the synergid cells begin to wither and die. The pollen tube forces through the synergids and releases the two sperm cells inside. One of the sperm cells travels to the egg cell and fuses with it producing the 2n zygote. The other sperm cell fuses with the central cell forming the 3n endosperm. The picture below depicts the ovule after double fertilization.
Step 2: Directly following fertilization the zygote nucleus will divide to form the embryo while the endosperm nucleus will divide to form the endosperm.
Step 3: The first division of the zygote results in a proembryo cell and a suspensor cell.
Step 4: The zygote continues to undergo mitotic divisions. One cell will elongate and form the suspensor which will support the embryo in the endosperm.
Step 5: After many mitotic divisions the embryo reaches the globular stage. After this stage the embryo will continue to divide and differentiate and will form two cotyledons (not pictured).
Step 6: The cottonseed has reached maturity. It has cotyledons, a seed coat (formed from the integuments), a shoot apex, and a root apex. |
To return to the fruit main page... |

Introduction Flowers&Fruit Roots Stems Leaves |